The remaining 50 items must be assigned to the higher price, the $15.00. Leveraging demand forecasting capabilities, you can gain insight into your changing inventory needs while also minimizing excess stock issues and obsolescence problems. Adopting a proactive FIFO approach supported by technologies and automation tools can help you enhance overall supply chain efficiency, resulting in improved customer satisfaction and cost savings.
FAQs About FIFO Method
- Under first-in, first-out method, the ending balance of inventory represents the most recent costs incurred to purchase merchandise or materials.
- Establish actionable and repeatable processes so your team can accurately and quickly identify older inventory items, understand expiration dates, and prioritize shipping based on FIFO standards.
- Without precise records, it’s impossible to correctly apply FIFO principles, which can lead to errors in financial reporting and inventory valuation.
- The 220 lamps Lee has not yet sold would still be considered inventory, and their value would be based on the prices not yet used in the calculation.
- Yes, FIFO is still a common inventory accounting method for many businesses.
A separate perpetual inventory card is prepared for each inventory item. This card has separate columns to record purchases, sales and balance of inventory in both units and dollars. The quantity and dollar information in these columns are updated in real time i.e., after each purchase and each sale. At any point in time, the perpetual inventory card can, therefore, provide information about purchases, cost of sales and the balance in inventory to date.
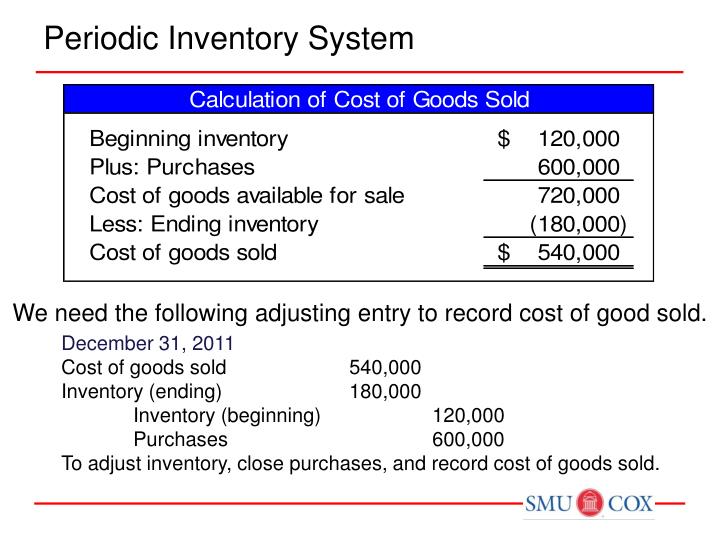
FIFO: Periodic Vs. Perpetual
If we apply the FIFO method in the above example, we will assume that the calculator unit that is first acquired (first-in) by the business for $3 will be issued first (first-out) to its customers. By the same assumption, the ending inventory value will be the cost of the most recent purchase ($4). FIFO, preferred under IFRS, showcases a stronger financial position by reporting lower COGS and thus higher net income, beneficial during inflation. Enhancing investor and lender perceptions by reflecting current market prices in inventory valuation may be most desirable in industries where asset valuation impacts financial health.
How Is the FIFO Method Calculated?
By assuming older stock is sold first, FIFO ensures the balance sheet reflects more recent purchase prices in inventory valuation. This offers a more precise valuation of current stock levels and enhances the accuracy of financial ratios and forecasts. It also aids in better inventory management by helping businesses make more informed decisions about restocking, pricing, and product lifecycle management. According to a report in The Wall Street Journal, 55% of S&P 500 companies use FIFO as their primary inventory method. While it’s useful to have a basic understanding of how to use the FIFO inventory method, we strongly recommend using accounting software like QuickBooks Online Plus. It’ll do all of the tedious calculations for you in the background automatically in real time.
This can happen when product costs rise and those later numbers are used in the cost of goods calculation, instead of the actual costs. One disadvantage of using FIFO is the increased risk of inventory obsolescence, especially if you manage rapidly changing or seasonal products. This is because FIFO prioritizes the sale of older inventory items before newer ones, which could lead to potential losses if more in-demand products don’t sell. Many businesses use FIFO, but it’s especially important for companies that sell perishable goods or goods that are subject to declining value. This includes food production companies as well as companies like clothing retailers or technology product retailers whose inventory value depends upon trends.
Now, let’s assume that the store becomes more confident in the popularity of these shirts from the sales at other stores and decides, right before its grand opening, to purchase an additional 50 shirts. The price on those shirts has increased to $6 per shirt, creating another $300 of inventory for the additional 50 shirts. This brings the total of shirts to 150 and total inventory cost to $800. Inventory is typically considered an asset, so your business will be responsible for calculating the cost of goods sold at the end of every month.
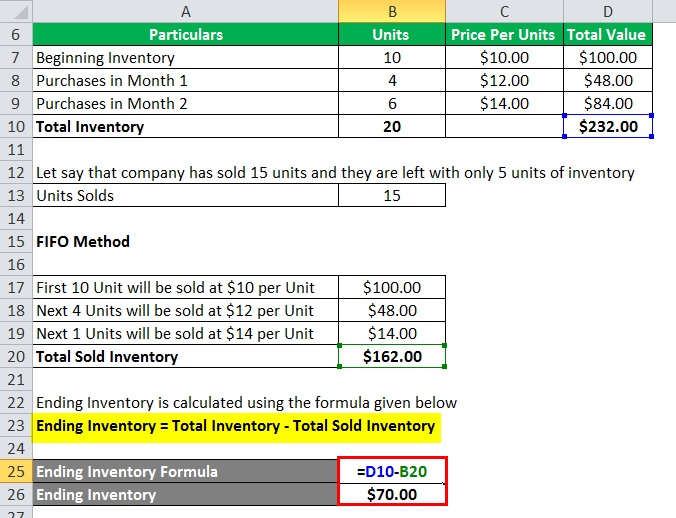
The price of the first 10 items bought as inventory is added together if 10 units of inventory were sold. The cost of these 10 items may differ depending on the valuation method chosen. There are balance sheet implications between these two valuation methods. More expensive inventory items are usually sold under LIFO so the more expensive inventory items are kept as inventory on the balance sheet under FIFO.
If you want to understand its use in a periodic inventory system, read “first-in, first-out (FIFO) method in periodic inventory system” article. It is also the most accurate method of aligning the expected cost flow with the actual flow of goods which offers businesses a truer picture of inventory costs. Businesses using the LIFO method will record the most recent inventory costs first, which impacts taxes if the cost of goods in the current economic conditions adjusting entries always include are higher and sales are down. This means that LIFO could enable businesses to pay less income tax than they likely should be paying, which the FIFO method does a better job of calculating. It makes sense in some industries because of the nature and movement speed of their inventory (such as the auto industry), so businesses in the U.S. can use the LIFO method if they fill out Form 970. FIFO is calculated by adding the cost of the earliest inventory items sold.
Under FIFO, inventory stock tends to be closely aligned with current market costs. In LIFO, however, balance sheet results may underrepresent the current value of inventory if prices have risen. FIFO helps businesses align the physical flow of goods with their representation on financial statements. The controller uses the information in the above table and the FIFO inventory method formula to calculate the cost of goods sold for December and the inventory balance as of the end of December. In such cases, you may want to explore other options such as the LIFO method (last-in first-out) and average cost methods.
Assume a company purchased 100 items for $10 each and then purchased 100 more items for $15 each. The COGS for each of the 60 items is $10/unit under the FIFO method because the first goods purchased are the first goods sold. Of the 140 remaining items in inventory, the value of 40 items is $10/unit and the value of 100 items is $15/unit because the inventory is assigned the most recent cost under the FIFO method. When properly implemented, FIFO helps companies streamline their inventory processes, enhance decision-making, and maintain clear financial records.